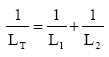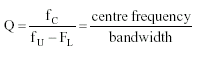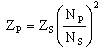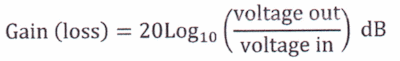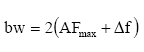|
Note
: Manipulation of the equation to find the missing
item may be needed in any of the following.
The
mathematical notation is being used where two letter
together means multiplied
eg.
P = VI is the same as P = V x I
|
Equation(s)
|
To calculate ????
|
Page
where
equation is discussed
|
|
R(total)
= R1 + R2 + R3
|
To find the total
resistance in series |
Click here |
|
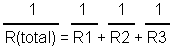
|
To find the total
resistance in parallel |
Click here |
|
P = VI, V = IR
|
To calculate
power, voltage, current, or resistance given any other
two. These have
been seen in the Foundation or Intermediate level
courses |
Click here |
|
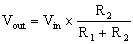
|
To calculate the
voltageout relative to the voltagein with
regards to a potential divider where R1 and
R2 represent the resistance value either
side of the centre. |
Click here |
|
P = V2 /
R, P = I2R
|
As above but this
set are new to the Advanced level. |
Click here
|
|
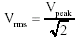
|
To calculate the RMS of a voltage which gives the
same heating effect as a direct current of the same
numeric value. |
Click here
|
|
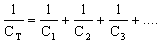
|
To calculate the
effective total capacitance of a number capacitors
linked in series |
Click here |
|
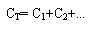
|
To calculate the
effective total capacitance of capacitors linked in
parallel, |
Click here |
|

|
To
calculate the value of a capacitor from area and
separation of the plates, permittivity of
dielectrics |
Click here
|
|
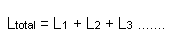
|
To calculate the
effective total inductance of a number inductors
linked in series |
Click here
|
|
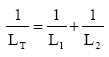
|
To calculate the
effective total inductance of a number inductors
linked in parallel |
Click here |
|
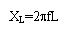
|
To
calculate the inductive reactance for a known
frequency and known inductance. |
Click here |
|
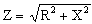 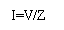
|
To
calculate the impedance from a combination of
resistance and reactance. |
Click here |
|
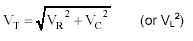
|
The supply voltage
Vtotal (VT) is thus the sum of the vectors through the
Resistor VR and Capacitor VC (or Inductor) |
Click here |
|
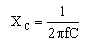
|
To
calculate the capacitive reactance for a known
frequency and known capacitance. |
Click here |
|
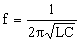
|
To calculate the
frequency of resonant a tuned circuit knowing the
value of the inductance and capacitance. |
Click here |
|
T
= 1 / f and f = 1 / T
|
To calculate the
time period of a sine wave at a particular frequency
or the frequency knowing the time period. |
Click here
|
|
T=CR
|
To
calculate the charging and discharging of a
capacitor in a CR circuit |
Click here
|
|
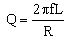 and and 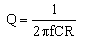
|
To calculate the Q
factor ( quality Factor) knowing the value of the
frequency, inductance and capacitance. |
Click here
|
|
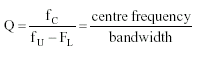
|
Calculation of the
Q of a tuned circuit, knowing the centre frequency,
and the upper and lower frequencies where the half
power points are noted. |
Click here |
|
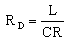
|
To calculate the dynamic resistance RD
knowing the value of the resistance, inductance and
capacitance |
Click here |
|
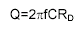
|
The relationship
between Q and Frequency, Capacitance, and Dynamic
Resistance |
Click here |
|
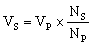
|
Formulas relating transformer primary Np
and secondary Ns turns to primary and
secondary potential differences Vs Vp
and currents Ip Is |
Click here |
|
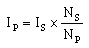
|
|
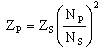
|
Formula
relating transformer primary Np and
secondary Ns turns to primary and
secondary impedances Zp Zs |
Click here
|
|

|
The two equation
mean the same hfe = 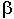 and is used to calculate the gain of
a transistor. and is used to calculate the gain of
a transistor. |
Click here |
|
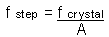
|
To calculate the
frequency step from the crystal frequency. |
Click here |
|
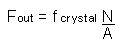
|
To calculate the
out going frequency from a frequency synthesizer. |
Click here |
|
c
= 3 x 108 m/s
|
speed of light But
this might be better remembered as
c = 300 x 106
m/s
|
Click here |
 |
The
equations relating to decibel power ratios. |
Click here |
|
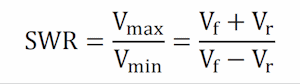
|
The
calculation of standing wave ratio (SWR) by
reference to VFORWARD and VREVERSE
|
Click here |
|
v
= f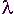
c
= f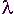
Please
note that sometimes v is used for the speed of light
and at other times c.
|
From the speed of
the velocity of light the wavelength can be determined
knowing the frequency or the frequency knowing the
wavelength. This was first introduced to you in chart
form in the Foundation Licence course. |
Click here |
|
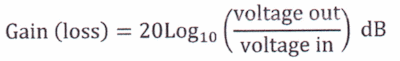
|
The
equations relating to decibel and voltage ratios. |
Click here |
|
Z02
= Zin X Zout
|
The formula
relating Z0 = the impedance of the
quarter-wave length of feeder matching line to the
impedance of the antenna Zin and the
impedance of the antenna Zout from the
matching line |
Click here |
|

|
To
calculate the field strength in volts /m given the
ERP and distance from the antenna. |
Click here |
|
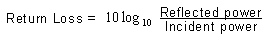
|
To calculate
return loss |
Click here |
|
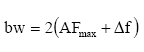
|
Bw is the
bandwidth requirement in relation to Af is the highest
modulating frequency and Δf is the carrier peak
deviation frequency |
Click here |
|
erp = power x gain (linear)
|
To calculate the
Effective Radiated Power (erp) from an antenna |
Used in the Intermediate course |
|

|
To calculate gain
of Yagi over a dipole |
Click here |
|
|